When visitors land on your website and see a Google warning message that says “Deceptive site ahead” or “The site ahead contains malware,” it can negatively impact your website and company. Imagine working hard on your website SEO and making your site land on the top search engine result page only to be met with one of these warning messages, ending in loss of traffic and possible business opportunity.
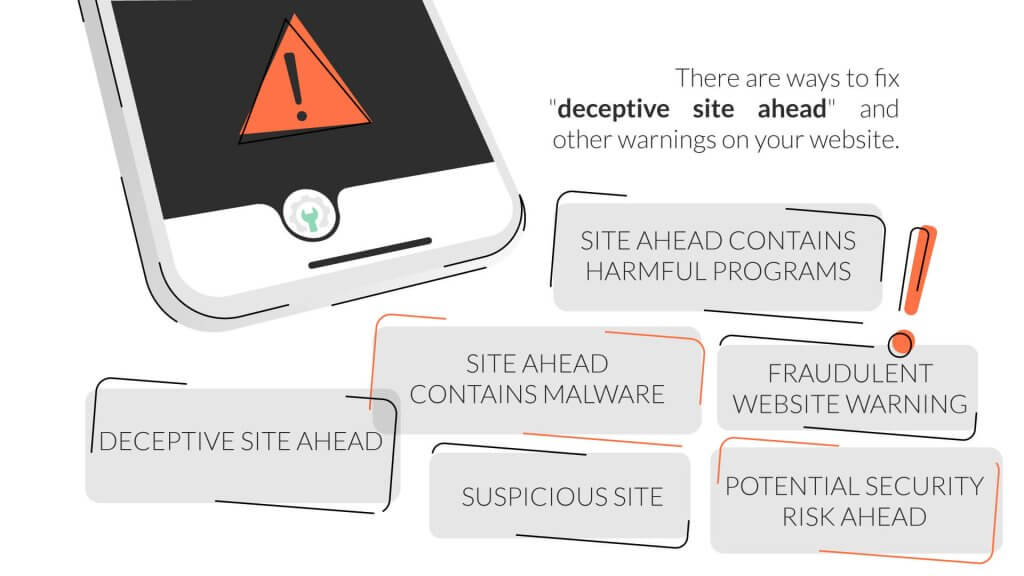
Even though these messages can be unnerving, there are ways to fix “deceptive site ahead” and other warnings on your website. In this article, you can find a detailed guide on what these warning messages mean, how you can fix them, and how to resubmit your website to Google.
- What Does ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ Mean?
- Causes for ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ Warning Messages on Your Website
- Types of Website Warning Messages and What They Mean
- How to Fix Website Warning Messages
- How to Resubmit Your Website to Google
- What if Your Website Doesn’t Pass the Review?
- What to Do About Warnings on Other Browsers
- How to Prevent ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ Warnings
What Does ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ Mean?
Finding out that Google is showing a warning message on your website can come as a shock to many, particularly when it’s happening to you for the first time. You might assume something is wrong with the system as you haven’t put anything dangerous or deceptive on the site. But it’s important to understand that someone else might have.
Once your website is open for public access, you’re open to outsiders, and the influence can be both negative and positive. Many website owners run regular security audits and take other measures to keep their websites as secure as possible.
Some major companies have been victims of cyberattacks, and according to the 2021 Data Breach Investigation Report, 46% of data breaches occur in small businesses. Regardless of how big or small it might be, any website can become a target for cyber-attacks. This makes it vital for small businesses to look into their cybersecurity.
Some common website hacks are URL injection, where a hacker builds spam pages on your website, and content injection, where a hacker adds relevant keywords and gibberish text onto the site.
If you see the warning message on your site, it indicates that your site has been hacked or you’ve followed a practice that Google doesn’t recommend. We’ll dig into the major reasons for this warning messaging in this article.
There’s a simple process that helps you get the warning message removed from your site. You need to resubmit your site back to Google and request them to unflag the site as dangerous or deceptive. However, before you do that, make sure the issues on your site are resolved.
Causes for “Deceptive Site Ahead” Warning Messages on Your Website
Generally, warning messages appear on a website because of an unauthorized user or hacker trying to intervene, a security misconfiguration, or a malware infection. However, there are several causes that can result in Google showing a warning message on your website:
- The website frontend is infected with malware, making your website redirect to some spammy site.
- Intentionally or unintentionally, your website is hosting phishing pages.
- The website has written some hidden backdoor code or script, which is being poorly read by the Google algorithm.
- There are some issues with your SSL certificate.
- The website might be stealing some sensitive user information, or it may be prone to malicious backlinking.
- There are some security vulnerabilities to your WordPress themes and plugins.
- There might be some suspicious downloads or questionable links on your website.
- There may be a possibility of some credit card malware practice on the website, such as on the payment check-out page. These malware practices are used to steal credit card data and send it to hackers.
Types of Website Warning Messages and What They Mean
“Deceptive site ahead” is not the only warning message you need to look for. While fixing and resubmitting your site remain necessary, the search engine can show different warning messages to your website, and they all have slightly different meanings attached to them.
Understanding the meaning of the warning messaging displayed on your website can help speed up the repair process. Let’s look at a few different warning messages that Google may attach to your website and understand what they mean.
“Deceptive Site Ahead”
As discussed above, there are multiple reasons why Google might be showing this warning on your site, like phishing pages. For example, there might be a webpage designed to look like part of your website, but it’s used to steal users’ personal or credit card information.
“Site Ahead Contains Malware”
This warning message indicates that the site may try to install some harmful software to your website visitor’s system. The malware could be anywhere on the website, like images, ads, or third-party components.
“Suspicious Site”
The suspicious site sign is a general warning which means Google has considered the site suspicious or possibly unsafe.
“Site Ahead Contains Harmful Programs”
The warning for harmful programs indicates that your site might try to trick website visitors into downloading programs that potentially cause problems for visitors.
“This Page is Trying to Load Script From Unauthenticated Sources”
If Google shows this warning on your website, it most likely means that your site is not hacked. The warning normally indicates that even though your site is HTTPS, it’s loading scripts from HTTP sources.
“Did You Mean {Website Name]?”
This message appears on your website when Google thinks that the users might be looking for a different website with a similar name or domain name. Sometimes hackers build sites similar to a safe website with just a single character difference. They do this to lure their visitors and trick them into giving their personal and sensitive data. However, fixing this problem is a bit different from the other warnings. When you’ve confirmed that this is the nature of the problem, you need to contact Google and inform them about the situation by filling out a form.
“Fraudulent Website Warning”
Even though Google Chrome easily takes about three-fourths of the global desktop market share, making it the most widely used web browser, there are still other players. This warning sign indicates the same message as the deceptive error in the Safari browser.
“Potential Security Risk Ahead”
Similarly, your website visitors see these warning messages when using the Firefox browser.
Even though Safari and Firefox use different words to warn about possible dangers and problems with websites than Google, their causes and fixes are the same.
How to Fix Website Warning Messages
Now that you understand different types of warning messages that can come from Google and what they mean, let’s discuss how you can fix these errors.
Before you can resubmit the site to Google for review, you must ensure the website security issues are fixed. Using the Google Search Console can offer a lot of help here. It allows you to easily find out what’s happening with your website and identify the issues, and you don’t need to be tech-savvy to use it.
If you’ve not yet set up the Search Console for your website, make sure you take some time to do it. It’s free, and it’ll help you monitor, manage, and improve your website performance even after the security warning issue is cleared.
Step 1: Check Your Security Issues Report via Google Search Console
Log into your Google Search Console account. If Google has located any security issues with your website, there will be a link given on the Overview tab of your Search Console account that will take you to a security issues report for your website.
You can also view this report from Security & Manual Actions and click on Security Issues on the sidebar.
Your security issues report will show you different possible security errors your website faces. However, Google identifies all security problems in three categories: hacked content, social engineering, and malware software. Let’s give a more detailed look into each category of security issues.
Hacked Content
Hacked content can be identified as any content on your website that’s added to the site without your permission and is causing security vulnerabilities. If a hacker has added any spammy links to any of your web pages, it will fall under hacked content.
For example, if your site has been hacked, your security issues report will include errors like:
- Hacked: Malware
- Hacked: Code injection
- Hacked: Content injection
- Hacked: URL injection
Social Engineering
The social engineering category of security issues indicates that your website content is trying to trick visitors into taking some dangerous or unwanted actions. If your website has any deceptive forms that make users provide their personal or confidential information, it will fall under social engineering issues. For example, having social engineering security issues on your report may include some of the following errors:
- Deceptive embedded resources
- Deceptive webpages
Malware and Unwanted Software
The malware and unwanted software category mean that you’ve applications or installable software on your site that can harm your website visitors. Either a hacker or the website owner could embed these into the website. For example, malware and unwanted software security issues in your report may show errors like:
- Links to harmful downloads
- Harmful downloads
Regardless of the security issues mentioned in your website report, you can click on it to get a more detailed analysis of your site.
Google also offers you advice on how you can solve these problems, but they’re often pretty technical. However, you can resolve many of these security issues with more straightforward and WordPress-friendly ways to fix the issues and remove the warning signs.
Step 2: Locate and Remove the Malicious Code on Your Website
Your hosting services can help you ensure that website security is effective. But if your web hosting service provider lacks this section, you can try to restore a previous and safe version of your website from the most recent site backup. That said, make sure you understand that restoring a previous website version means you’ll lose any changes and updates you might have made since the last backup.
If you don’t have a backup or don’t want to lose the changes you’ve made since the last backup, you can use different backup plugins or automated website backup services for your website.
You can avoid stress by opting for the right hosting services. HostPapa’s managed WordPress hosting services help ensure your website is secure and backed up.
Step 3: Make Sure Your Website SSL Certificate is Properly Installed
An SSL certificate is vital for your website’s SEO and overall performance. It’s one of the web security protocols that help with encryption and authentication of data when sent between two applications, such as a browser and web server.
However, when your SSL certificate isn’t properly installed, it can cause Google to attach a warning message to your website. You can check the installation effectiveness with tools like SSL Checker.
Often, your hosting service provider offers website security features like Cloudflare integrations, including a free SSL certificate.
Step 4: Redirect Your Website From HTTP to HTTPS
Your website SSL certificate enables HTTPS for your site. As a best and standard practice, all websites should be using HTTPS, as it’s better for your SEO, it’s more secure, and it’ll get you more accurate referral data. However, transferring your website from HTTP to HTTPS can cause some issues.
It’s important that you permanently redirect all your HTTP traffic to HTTPS. If your website is running on HTTPS, but some webpages are loaded on a less secure HTTP connection, it may make Google leave a warning message on the site. However, your hosting service provider can help you fix this issue depending on their server software.
You can solve this issue by using a WordPress plugin to configure your website to redirect to HTTPS. Once you’ve confirmed the correct installation of the SSL certificate, download the Really Simple SSL plugin to help you run your website over HTTPS.
Remember that using a plugin isn’t recommended as a permanent solution. Even though using third-party plugins offers a quick solution, which can be tempting, introducing them to your website, in the long run, can open the site to an extra layer of risk.
How to Resubmit Your Website to Google
Once you’ve figured out your website’s security problems and cleaned it up, the next step is to resubmit it to Google for review. Make sure to follow the given steps to resubmit your website to Google.

Step 1: Make Sure Your Website is Ready for Submission
Just to avoid any more issues, double-check if you’ve completely removed the harmful content from your website. If you previously used a security scanner to find the security issues, rerun it on the site.
If you resubmit the site without resolving all the problems, it may lead to additional delays.
Google needs to be able to crawl your site to review it, so make sure you haven’t blocked Googlebot. Also, ensure your website is live for Google to check if you’ve brought it offline to fix the hacking issues.
Step 2: Request a Review From Google
Once your website is ready for review, go back to Google Search Console and click on Request Review under Security Issues Report.
It will take you to a new form where you will have to describe how you fixed the issues with the site. Make sure you write a sentence for each security issue identified and explain how you fixed it.
Step 3: Wait for Google’s Response
How long Google takes to review your website and give you feedback depends on what type of security issues were identified on the site. For example, hacking with spam may take a couple of weeks, malware may take a few days, and phishing might just take a day.
If Google finds that your website is completely clean from all security issues, they may remove the warning message from the website within 72 hours or the review request.
What if Your Website Doesn’t Pass the Review?
If Google finds that you have not fully resolved the problem, the warning message will continue to show on the site. You can recheck your security issues report, and it might include more infected URLs from your site to help you track down any malicious content. Once you can be sure the problems are resolved, you need to repeat submitting your website to Google.
What to Do About Warnings on Other Browsers
If your website is showing warnings on other browsers, like Safari and Firefox, fortunately, there are ways to fix this. You don’t need to go through an individual review process for every browser. Like many other browsers, Safari and Firefox get information from Google Safe Browsing lists, a group of frequently updated lists of unsafe web sources. When you get your website cleared from Google, the warning signs are most likely to be removed from other browsers.
How to Prevent “Deceptive Site Ahead” Warnings
Whether you want to believe it, no website is 100% secure. New hacking tricks are always popping up, and as a website owner, you’re always running the risk of being the next victim.
However, you can prevent the majority of cyber-attacks and security issues by following some standard best web practices.
Let’s look at some of the best practices website owners should be following to avoid getting that red warning message on their site to greet their visitors.
Keep Your Website Up-To-Date
All resources on your website, like the core CMS program, theme, and plugins, must be up-to-date. Even though developers keep updating the software to be able to run through new security threats, if you’re operating on an old version, your website is still vulnerable.
According to a study at the time of infection, 49% of hacked WordPress websites were operating on outdated versions of the CMS. Updating your website plugins is just as important. Plugins are one of the essential features of WordPress, but it’s straightforward to download a bunch of them into your website and forget about them.
Each plugin you install is potentially an access point to your website for a hacker. To prevent security breaches and be as safe as possible, update them regularly and don’t keep plugins you’re not using.
Use WordPress Security Plugins
You can find a comprehensive list of WordPress plugins designed to improve your website security, but some of these plugins can cause your website performance and possibly security issues. It’s important to identify the WordPress security plugins that you can trust and only use those for your website for the best results.
Monitor Your Google Search Console Account
Website owners who have an account on Google Search Console receive emails for any warnings about security issues. You can keep an eye on any emails from Google Search Console for website security warnings or check them from time to time.
Besides, Search Console also offers other features to help you with your website performance and search engine optimization. You can get many benefits by keeping up with this tool to make your website better.
Restrict Access
It can be surprising how easily hackers can access your website. At times, the simple use of your password to get to your website. Be very careful about who you can trust with the login credentials of your website. Restrict the access to a small group of trusted team members and make sure everyone in your team is following the best-recommended practices for website security, like using a password manager. It also helps to understand how they can prevent scams like phishing emails.
Select a Secure Host
As a website owner, you should avoid any action that makes your website more vulnerable to security and performance issues. Regardless of how tempting free hosting services may sound, often it turns out to be a bad idea. To get server-level security for your website, you need to choose a hosting service provider that you can trust.
Following are some of the features and services to look for in your website host that can help keep the warning message off your website.
- Provide automatic updates for all security releases
- Protect your website via firewalls like Cloudflare
- Offer automatic website backups
- Uses a two-factor authentication feature
Summing It Up
It can be alarming to realize that Google has set a warning message on your website, especially when this is happening to you for the first time, but it’s not hard to fix. The warning messaging works as a helpful alert that tells you something is wrong with your website.
The next time you wake up to a warning message, your first response should gear up and try to resolve all issues as soon as possible. To keep your losses to a minimum, keep an eye on your Google Search Console and monitor it.
An even better practice would be to run regular security audits on your website and avoid such security issues in the first place. You can do this by following the security best practices for WordPress websites and the preventive measures discussed above. They can help you go a long way in keeping your website safe and ready to welcome all incoming traffic. However, make sure you understand that website security is important at all levels, including your hosting, so make sure you have all areas covered to protect your site.